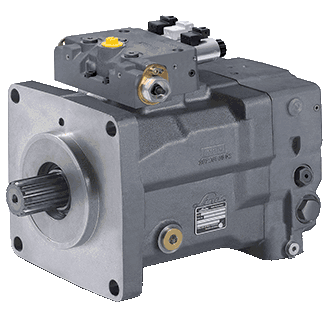
Hydraulic pumps
Selling hydraulic pump
The sale of types of hydraulic pumps include hydraulic gear pumps, hydraulic vane pumps, axial and radial hydraulic piston pumps, hydraulic unit gear pumps, variable flow cartridge pumps, variable flow piston pumps and hydraulic hand pumps. Please, to access technical information and Hydraulic pump price, click on the desired product.
How to choose a hydraulic pump
The first thing that should be taken into consideration when choosing the right hydraulic pump for a specific application is to check the amount of pressure and current required in the circuit, so the flow and pressure curve must be calculated in a time cycle, and in this regard, the simultaneity of consumption in different related factors must be determined. to determine the required current as much as possible. To choose the right hydraulic pump, you should pay attention to the following:
Adding ten percent of the flow rate to the flow rate determined in pump sizing
In the safety valve or pressure relief valve, the regulation pressure should be equal to ten percent more than the working pressure of the system.
Finally, these two factors cause more power to be applied in the hydraulic injection system.
What acts as the driving force in hydraulic systems are combustion engines or electric motors. The speed range defined for the electric motor is between 1200 and 1800 rpm; Of course, it should be noted that in air and space applications, the pump is also used with a speed of 2000 rpm. In cases where the system is mobile or there is a problem of lack of space and also the weight and volume characteristics of the pump are important, small units with high speed should be used.
Calculation of the required power for the electric motor driving the pump in hydraulic systems (by determining the working pressure and oil flow rate and without considering the mechanical and volumetric efficiencies)
P (kilowatt) = [Q (lit/min) X p (bar)]/600 where in this formula P = power, Q = flow rate, p = pressure.
What is a hydraulic pump?
Hydraulic pump is one of the two main parts of the hydraulic system and it supplies its power from an electric motor or a combustion engine. Hydraulic pumps receive (suction) non-pressurized fluid from the hydraulic powerpack tank (tank) and then deliver the high-pressure fluid to a hydraulic system with the power they receive from the energy source (electric motor or combustion engine). Due to the importance of the hydraulic pump, it is also called the heart of the hydraulic system.
Division of hydraulic pumps
In the hydraulic industry, pumps are divided into the following two general categories.
- Negative displacement pumps (hydrodynamic pumps)
- Positive displacement pumps
Advantages of hydraulic pumps with positive displacement (compared to the type with non-positive displacement)
- Ability to work at high pressures (up to 10000 psi and above)
- Small and compact dimensions
- High volumetric efficiency
- Slight change in efficiency in Designed pressure range
- High flexibility (ability to work in a wide range of required pressures and speeds)
Hydraulic pumps with positive displacement are divided into three main types:
Gear pumps
vane pumps
piston pumps
Gear pumps (with fixed displacement)
- External gear pumps
- Internal gear pumps
- Earring pumps
- Screw pumps
- Gyrotor pumps
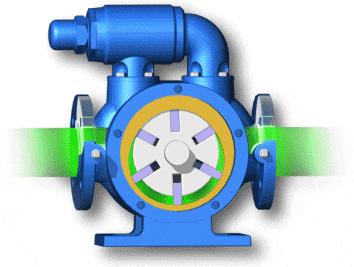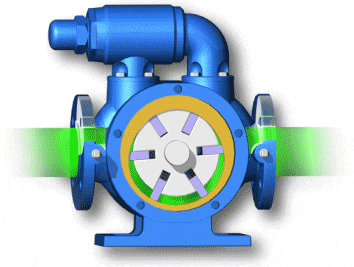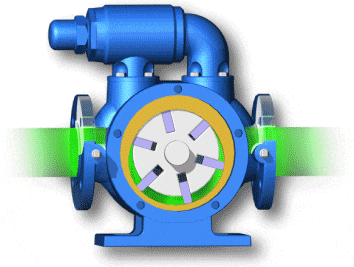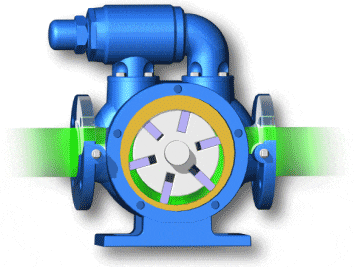
vane pumps (with fixed or variable displacement)
- Unbalanced vane pumps (with fixed or variable displacement)
- Balanced vane pumps (only with fixed displacement)
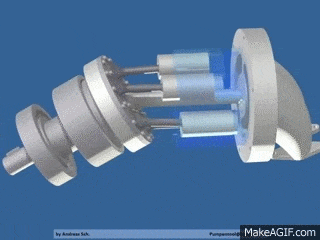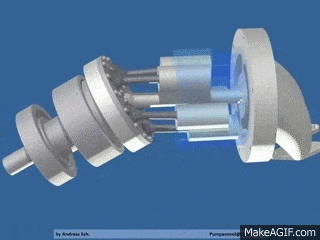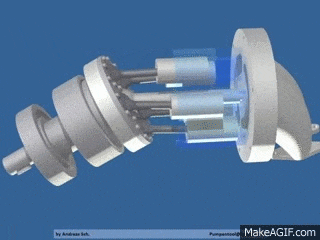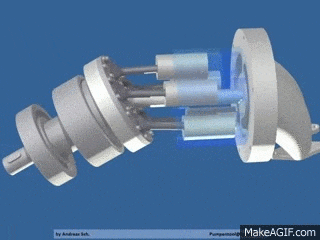
Piston pumps (with fixed or variable displacement)
- Axial piston pumps
- Radial piston pumps
Efficiency of hydraulic pumps
The efficiency of a pump generally depends on the amount of tolerances and precision used in the construction, the mechanical condition of the components and the pressure balance. In an ideal pump, the leakage between the involved components is considered to be zero in theory. In practice, the leaks should be as small as possible so that it is possible to create a thin film of oil to lubricate the sliding parts.
The overall efficiency of the pump is calculated by comparing the power available at the output and the power consumed at the input and is divided into volumetric and mechanical efficiency.
volume efficiency
Volume efficiency determines the amount of leakage in the pump. This amount is related to the situations where the pump is in the designed tolerance conditions, working conditions and design pressure.
Mechanical efficiency
Mechanical efficiency specifies the amount of energy loss due to factors such as friction in bearings and involved components, as well as disturbance in the fluid. The mechanical efficiency of pumps is usually between 90 and 95%.
Total return
Total efficiency specifies the total energy loss and is equal to the product of volume and mechanical efficiency.
Hydraulic pump selection criteria
- Maximum working pressure
- Accessibility and replacement of components
- Maximum output flow rate
- Maintenance and spare parts
- Type control
- drive speed
- fluid type
- noise
- size and weight
- required tolerances
- yield
- price
In order to protect the pump against cavitation and keep the pressure higher than the fluid saturation pressure at the pump inlet, it is necessary to observe the following materials:
- The speed of the suction line should be considered less than 5 ft/sec
- The pump inlet lines should be selected as short as possible
- Minimum fittings should be used in the inlet line
- The pump should be installed as close to the tank as possible
- Use filters with low pressure drop and pollution index so that they can be replaced when they become dirty
- Use the appropriate oil introduced by the manufacturer.